[Updated January 2024] The cryptocurrency and blockchain industry has the potential to transform several industries. Board members are urged to proactively understand key themes, including disruptions, opportunities, legal considerations, risks, and industry dynamics, as the sector evolves.

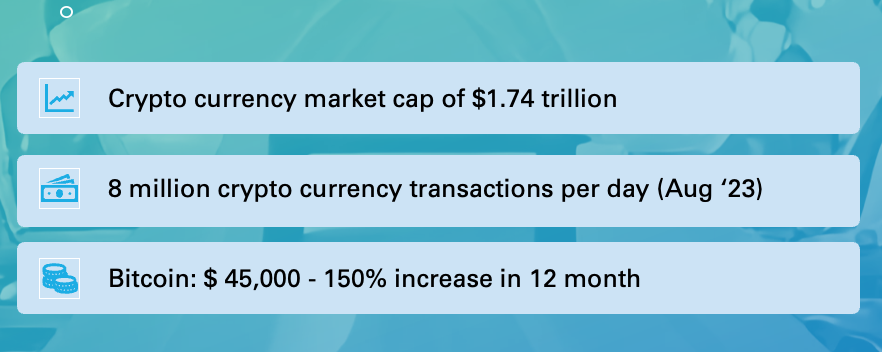
The cryptocurrency and blockchain industry has the potential to reshape our perspectives on money, ownership, and trust. Cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology facilitate faster, cheaper, and more secure transactions, extending beyond digital currencies to include ICOs, STOs, and NFTs, among others. The current market cap of cryptocurrencies and blockchain tokens is approximately $1.76 trillion, representing nearly 2% of all global money.
As of August 2023, major cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin, Ethereum, Ripple, Cardano, Dogecoin, and Tron are experiencing over 8 million daily transactions, a significant increase compared to August 2016.
Back in 2015, the World Economic Forum predicted that by 2027, around 10% of the global gross domestic product (GDP) would be stored on blockchain technology. Current trends indicate that this projection is on track. Notably, recent SEC approvals for cryptocurrency ETFs and new regulations like the European MiCA (Markets in Crypto-Assets) regulation are expected to further propel the crypto industry.
While the cryptocurrency and blockchain industry is still in its infancy, it is crucial for members of the board of directors to delve into key themes before these factors impact a company’s business model. It is recommended to gain insights into potential disruptions, new business opportunities, basic concepts and technologies, relevant laws and regulations, potential risks, and the dynamics of an emerging industry.
1. Potential disruption of several industries
There are several industries that are potentially disrupted by cryptocurrencies and blockchain technologies. Members of the board of directors should observe the following industries and look for signs of disruption.
Supply chain management: Blockchain technology can enable increased transparency and security in supply chain management, allowing for more efficient tracking of goods and materials.
Real estate: Blockchain technology can be used to create a more efficient and transparent system for buying and selling property, as well as for tracking and managing property ownership.
Healthcare: Blockchain technology can be used to securely store and share medical records, as well as to facilitate more efficient and secure communication between healthcare providers.
Gaming & entertainment: Cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology can be used to enable new forms of digital ownership and monetization of in-game assets.
Retail: Cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology can be used to enable secure and transparent transactions between retailers and customers, as well as to improve supply chain management and inventory tracking.
Financial services: Cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology have the potential to disrupt traditional financial services by providing a more inclusive and accessible way for individuals and businesses to access financial services, such as banking and payments.
2. New business opportunities
Cryptocurrencies & blockchain technologies have the potential to enable a wide range of new business opportunities. Some of the most relevant examples include:
Supply Chain Management: Blockchain can be used to create transparent and tamper-proof records of transactions in supply chain management, allowing for increased trust and efficiency.
Digital Identity: Blockchain can be used to create secure and decentralized digital identities, allowing for greater privacy and control over personal information.
Gaming: Blockchain can be used to create decentralized and transparent in-game economies, allowing for true ownership of virtual assets.
Tokenization: Blockchain can be used to tokenize assets such as real estate, art, and other collectibles, making it possible to buy and sell fractions of these assets.
Payment: The use of cryptocurrency as a form of payment enables faster and cheaper transactions, especially cross-border transactions.
Crowdfunding: Blockchain can be used to create decentralized crowdfunding platforms, allowing for more transparent and efficient fundraising for projects.
Internet of Things: Blockchain technology can be used to create secure and decentralized networks for the Internet of Things (IoT), allowing for greater trust and control over the exchange of data.
Decentralized finance (DeFi): Blockchain technology can be used to create decentralized financial services, such as lending and borrowing platforms, that operate independently of traditional financial institutions.
3. Basic concepts & technologies
It is recommended to introduce the basic concepts and technologies behind cryptocurrencies and blockchain to the members of the board of directors. Decentralization, immutability, transparency, cryptography, smart contracts, distributed ledger, limited supply, anonymity, borderless and digital are the most central ones.

Decentralization: Blockchain technologies and respective cryptocurrencies are decentralized, meaning they are not controlled by any single entity or organization. Crypto currencies are not controlled by any central authority such as a government or central bank. This allows for increased autonomy and control for users over their own funds.
Immutability: Once a transaction is added to a block and the block is added to the blockchain, the information in that block cannot be altered. This ensures the integrity and immutability of the data and crypto currency transactions stored on the blockchain.
Transparency: Blockchain technology allows for increased transparency by providing a public, tamper-proof record of all crypto currency transactions.
Cryptography: Blockchain and crypto currencies use cryptography to secure and protect transactions, making it a secure technology for storing and sharing sensitive information. This also ensures the integrity and security of crypto currencies.
Smart Contracts: Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement between buyer and seller being directly written into lines of code. These contracts can be stored and replicated on the blockchain network.
Distributed Ledger: A distributed ledger is a database that is spread across a network of computers. Each copy of the database is identical and is updated simultaneously.
Limited supply: The total supply of most cryptocurrencies is limited, meaning that there is a maximum number of units that can be created. This can help to prevent inflation and ensure the value of the currency remains stable.
Anonymity: Cryptocurrencies can provide a high level of anonymity for users, as transactions are recorded using a public key rather than a name or personal information.
Borderless: Cryptocurrencies can be sent and received from anywhere in the world, and the transaction can be done almost instantaneously, regardless of geographical boundaries.
Digital: Blockchain & cryptocurrencies exist only in digital form and are stored and transferred electronically.
4. Relevant laws & regulations
Members of the board of directors should consider a number of laws and regulations related to cryptocurrencies and blockchain when developing their policies and procedures. It is important to note that the laws and regulations surrounding cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology vary by jurisdiction.
In June 2023, the European Union implemented one of the most advanced crypto regulations: 'MiCA' - The Markets in Crypto Assets Regulation.
Some of the most relevant general laws are AML, KYC, taxation, securities, GDPR and smart contracts regulations:
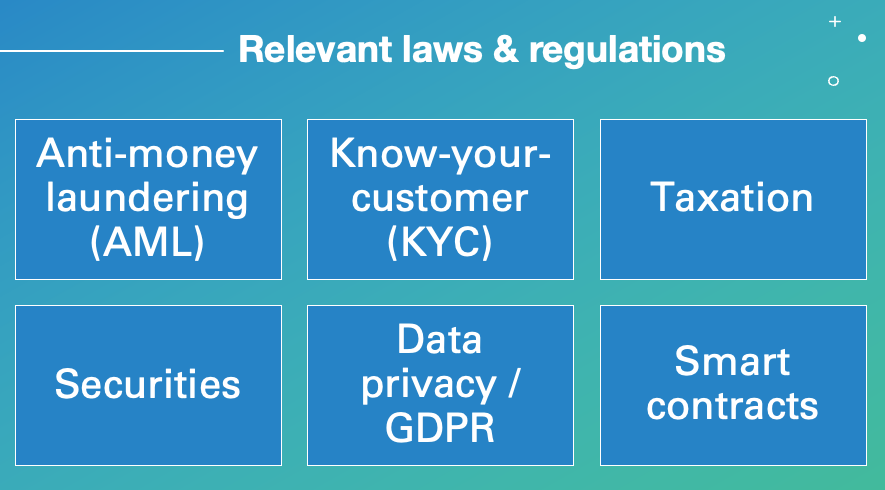
Anti-money laundering (AML) laws: These laws aim to prevent the use of cryptocurrencies for illegal activities such as money laundering and terrorist financing.
Know-your-customer (KYC) regulations: These regulations require cryptocurrency exchanges and other companies to verify the identity of their customers.
Taxation laws: Different countries have different tax laws for cryptocurrencies, and it is important for individuals and businesses to comply with these laws to avoid penalties.
Securities laws: Some jurisdictions consider certain cryptocurrencies to be securities, and they are subject to securities laws and regulations.
Data privacy laws: As blockchain technology is used for storing data, it is important for companies to comply with data privacy laws such as the
General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union.
Smart contracts regulations: Smart contracts, which are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement between buyer and seller being directly written into lines of code, also fall under scrutiny and regulations.
Given that the crypto & blockchain industry is still at early stage the surrounding laws and regulations are constantly evolving and it is essential to stay informed of updates and changes in order to comply with them.
5. Potential risks
Cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology can bring several potential risks to a company.

Security risks: Cryptocurrencies and blockchain transactions are vulnerable to hacking, fraud, and other types of cyber attacks, which can lead to financial losses for the company.
Compliance risks: Cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology are still largely unregulated, and companies may not be fully aware of the legal and compliance requirements related to their use.
Volatility risks: The value of cryptocurrencies can be highly volatile, which can lead to significant financial losses for a company if they are holding a significant amount of cryptocurrency assets.
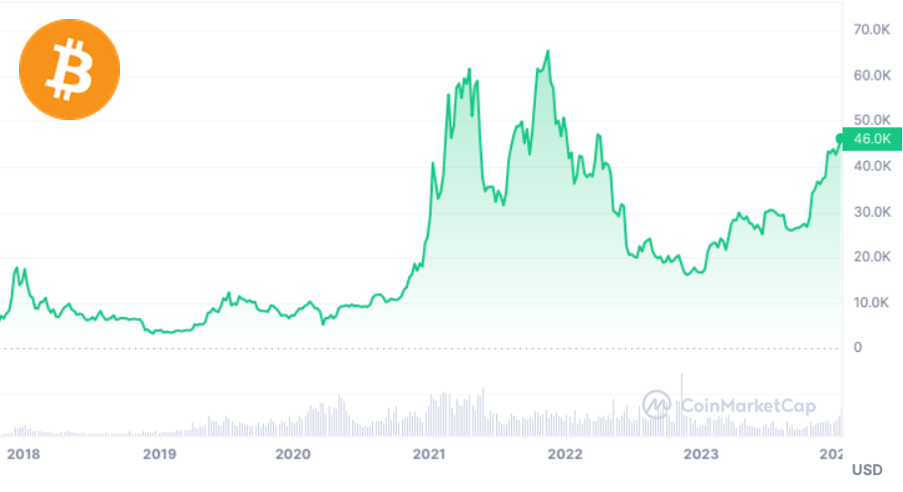
Source: CoinMarketCap.com
Operational risks: Implementing and using blockchain technology can be complex and may require significant resources and expertise, which can lead to operational challenges and disruptions for a company.
Reputational risks: Companies that are associated with cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology may be perceived as risky or untrustworthy by some customers, investors, and partners.
6. Dynamics of the early industry
The early cryptocurrency and blockchain industry sometimes feel like Wild West and has several key dynamics that members of the board of directors should be aware of.
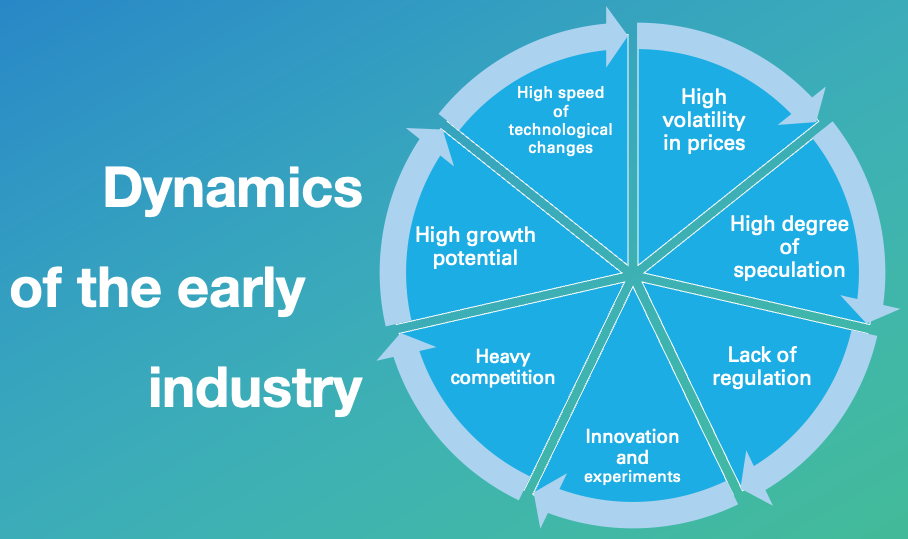
High volatility in prices, as the market is still relatively new and uncertain.
A high degree of speculation, as many investors buy cryptocurrencies in the hopes of making a quick profit.
A lack of regulation, which has led to a Wild West atmosphere and a lack of protection for investors.
Innovation and experimentation, as many companies and individuals are working to find new use cases for blockchain technology.
Heavy competition, as there are many different cryptocurrencies and blockchain projects vying for market share.
High growth potential, as the technology is still in its early stages and has the potential to disrupt a wide range of industries.
High speed of technological changes with new crypto currencies and different blockchain versions coming up every now and then.
Finally, it's worth noting that while the crypto-currencies and blockchain industry is still in its early stages, regulations and institutional involvement have been increasing which may change the dynamics of the industry.
https://FrankSchwabSpeaks.com
Credits:
Some icons are created by Freepik – Flaticon, https://www.flaticon.com
Presentation is supported by Microsoft Powerpoint, http://www.Microsoft.com
Some text is supported by ChatGTP, http://chat.openai.com
Some pics are supported by Craiyon, https://www.craiyon.com
Some pics are based on CoinMarketCap, https://CoinMarketCap.com